IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™
Most people want to “eat healthy,” but no one explains what nutrients actually do, how they work together, and how to choose foods that truly support the body.
You are told to:
“Add protein”
“Take vitamin D”
“Increase iron”
But no one shows the system behind it.
We are taught to count calories.
We are not taught to understand the importance of nutrients.
So we created something we wish every person had at the very start of their health journey:
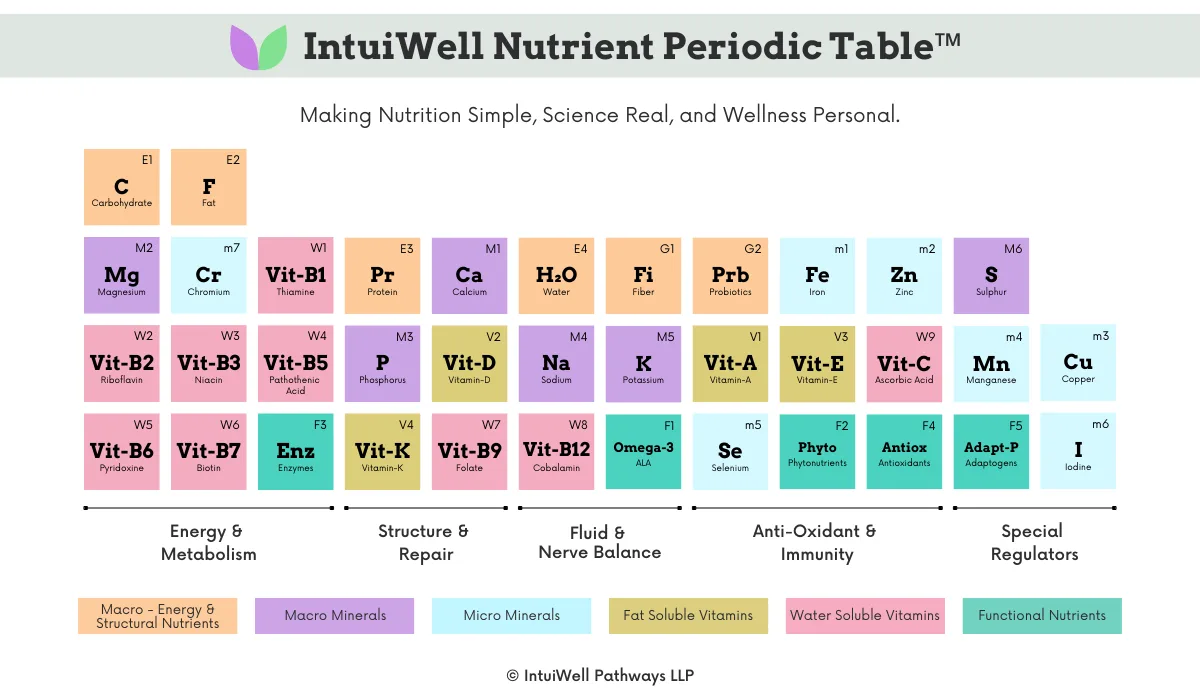
The IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™
A clean, colour-coded, science-backed nutrient map that finally shows:
What each nutrient does
Where to find it in an Indian diet (plant and animal sources)
How nutrients help or block each other
What your body actually needs (Indian RDA as per ICMR–NIN)
How to pair foods so your health improves naturally
It is simple enough for beginners.
It is detailed enough for professionals.
It is clear enough for anyone who wants to take charge of their wellbeing — one nutrient at a time.
A Quick Note Before You Start
This guide is for education, not for diagnosis or treatment.
RDAs are based on ICMR–NIN guidelines (latest available) and vary by age, sex, and life stage.
Always talk to your doctor or qualified nutritionist before starting supplements or making major dietary changes, especially if you have a medical condition or take medication.
Table of Contents
1. What Is the IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™?
The IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™ is a visual, colour-coded cheat sheet that shows:
- Every key nutrient
- Its main function
- Its Indian food sources (plant and animal)
- What boosts its absorption
- What blocks or interferes with it
Think of it as a periodic table for nutrition — designed for real people, real Indian plates, and real life.
2. Why We Created This for Indian Diets
Most nutrition charts:
- Focus on Western foods
- List nutrients without context
- Ignore how nutrients help or block each other
In India, many people:
- Eat mostly vegetarian meals
- Struggle with low B12, D, iron, magnesium
- Get flooded with “tips” but no clear system
We wanted one tool that:
- Uses Indian foods first
- Focuses on how the body actually uses nutrients
- Shows boosters and blockers in one glance
That tool is the IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™.
3. How to Read the Table: The 5 Functional Columns
Every nutrient in the table sits in one of five functional columns and 6 color families based on its main role in your body.
Column 1 – Energy & Metabolism
Carbohydrates, protein, fats, fibre, and water — everything your body runs on.
They:
- Provide energy
- Support brain and muscle function
- Keep digestion and metabolism going
Column 2 – Structure & Repair
Macro minerals that build and maintain:
- Bones
- Teeth
- Connective tissues
- Enzymes and basic cellular structures
Column 3 – Fluid & Nerve Balance
Electrolytes that keep:
- Hydration in balance
- Blood pressure stable
- Nerves and muscles firing correctly
Column 4 – Antioxidant & Immunity
Vitamins and minerals that:
- Protect your cells
- Reduce oxidative stress and inflammation
- Support immune function
Column 5 – Special Regulators
Functional nutrients that:
- Support gut health
- Modulate hormones
- Reduce chronic inflammation
- Support longevity and long-term resilience
These columns tell you what your plate is doing for your body.
4. Colour Codes: The 6 Nutrient Families
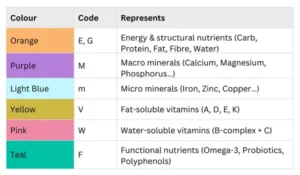
Each colour in the IntuiWell table instantly tells you what kind of nutrient you are looking at.This makes the table instantly readable, even for someone with no nutrition background.
5. What Each Nutrient Tile Shows
Every nutrient follows one simple, universal format:
- Stands for – what the nutrient is
- Function – what it does in your body
- Plant Sources (Indian) – key plant-based foods
- Animal Sources (Indian) – key animal-based foods
- Enhances Absorption / Impact – what to pair with
- Interferes / Blocks – what reduces absorption or effect
- Quick Note – a simple, real-life reminder
- Indian RDA – as per ICMR–NIN (shared on the downloadable table and detailed nutrient pages)
So instead of hunting across articles and searches, you finally have everything in one framework.
6. Nutrients in the IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™
Note: This pillar page gives you a 30-second summary of each nutrient.
Each nutrient will have a separate, detailed article linked from here.
6.1 Macro – Energy & Structural Nutrients (Orange)
Stands for: Your body’s primary and most accessible energy source.
Function:
- Fuels the brain, red blood cells, and active muscles
- Prevents your body from breaking down protein for energy
Plant Sources (Indian):
Millets (ragi, bajra, jowar), brown/red rice, whole wheat, oats, potatoes, fruits, vegetables, jaggery, honey.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Minimal; mainly indirect from mixed dishes (e.g., milk-based sweets with added sugar or grains).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Pair with protein + fibre to slow glucose release and stabilise energy.
Interferes / Blocks:
Refined sugar, low-fibre meals, ultra-processed carbs → glucose spikes and crashes.
Quick Note:
Carbs are not the enemy. Quality, quantity, timing, and fibre matter.
E2 — Healthy Fats (F)
Stands For: Essential fats for brain, hormones, skin, and vitamin absorption.
Function:
Build cell membranes, produce hormones, support brain function, and help absorb vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Almonds, walnuts, chia, flaxseed, groundnut, groundnut oil, mustard oil, coconut, avocado, sesame.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish (rohu, mackerel, sardines), ghee, butter, full-fat dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Eat with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess omega-6 fats, trans fats, repeated oil heating.
Quick Note:
You need fat. Choose the right types and amounts.
E3 — Protein (Pr)
Stands For: The body’s building and repair material.
Function:
Builds muscles, enzymes, hormones, and immune molecules.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Lentils, dals, chickpeas, kidney beans, soy, tofu, paneer (for lacto-vegetarians), sprouts, quinoa, curd.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, chicken, fish, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Combine plant proteins (e.g., dal + rice, chole + rice, roti + paneer) for better amino acid balance.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very low-calorie diets and severe carb restriction can make the body burn protein for energy.
Quick Note:
Aim for protein in every meal — especially breakfast.
E4 — Water (H₂O)
Stands For: The fluid that runs your entire internal system.
Function:
Regulates temperature, digestion, nutrient transport, and detox.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Plain water, herbal teas, soups, coconut water, water-rich fruits and vegetables.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Broths and soups made with chicken, fish, or eggs.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Add electrolytes (like salt and potassium) in heat or after heavy sweating.
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess caffeine, alcohol, and very high-salt diets.
Quick Note:
Most people are mildly dehydrated and do not realise it.
G1 — Fibre (Fi)
Stands For: The non-digestible carbohydrate your gut thrives on.
Function:
Slows sugar absorption, feeds gut bacteria, supports bowel movement and detox.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, flaxseed, chia, legumes, millets, psyllium husk.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Negligible; fibre is almost entirely plant-based.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Fibre + adequate water = best digestion.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very high fibre with poor hydration → constipation and bloating.
Quick Note:
Your microbiome lives on fibre. Feed it daily.
G2 — Probiotics
Stands For: Live gut bacteria that support immunity and digestion.
Function:
Maintain a healthy microbiome, support digestion and immune function.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Curd, buttermilk, dosa/idli batter, kanji, homemade pickles, fermented vegetables.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Yogurt, kefir (where available).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Work best with fibre (prebiotics).
Interferes / Blocks:
High sugar, frequent antibiotics, ultra-processed diets.
Quick Note:
Diversity of strains and foods matters more than high capsule doses.
6.2 Macro Minerals (Purple)
M1 — Calcium (Ca)
Stands For: The bone and muscle mineral.
Function:
Bone strength, muscle contraction, nerve signalling, blood clotting.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Ragi, sesame seeds, leafy greens, fortified plant milks.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Milk, curd, paneer, cheese, eggs, fish with bones (like sardines).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Vitamin D and K2 improve calcium utilisation.
Interferes / Blocks:
High-dose iron taken with calcium, excess caffeine.
Quick Note:
Do not take calcium supplements blindly. Test vitamin D and discuss with a professional.
M2 — Magnesium (Mg)
Stands For: The relaxation and enzyme mineral.
Function:
Muscle relaxation, nerve function, glucose regulation, and co-factor for 300+ enzymes.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Pumpkin seeds, almonds, spinach, jaggery, whole grains, legumes.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Fish, eggs, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Vitamin B6 and good hydration.
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess sugar, alcohol, chronic stress.
Quick Note:
Many people are likely low in magnesium, especially with high stress and refined diets.
M3 — Phosphorus (Ph)
Stands for: Energy and bone mineral.
Function:
ATP production, bone structure, cell membranes.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Dairy, legumes, nuts, whole grains.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Balanced calcium intake.
Interferes / Blocks:
Processed foods high in phosphate additives.
Quick Note:
True deficiency is rare. Imbalance with calcium is more common.
M4 — Sodium (Na)
Stands For: The fluid and nerve mineral.
Function:
Fluid balance, nerve conduction, muscle contraction.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Iodised salt, soups, pickles, fermented foods.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Salted eggs, salted fish, broths.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Balanced with potassium.
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess ultra-processed foods and salty snacks.
Quick Note:
Sodium itself is not the enemy. Excess processed salt is the problem.
M5 — Potassium (K)
Stands For: The blood pressure and hydration mineral.
Function:
Heart rhythm, muscle function, fluid balance.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Banana, coconut water, potatoes, spinach, rajma, lentils, fruits.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, chicken (moderate).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Good hydration + adequate magnesium.
Interferes / Blocks:
Consistently high sodium intake.
Quick Note:
Potassium naturally counters many harmful effects of excess sodium.
M6 — Sulfur (S)
Stands For: Detox and protein-structure mineral.
Function:
Supports glutathione production, detox pathways, and connective tissue.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Garlic, onion, cabbage, broccoli, other cruciferous vegetables, legumes.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Vitamin C supports sulfur pathways.
Interferes / Blocks:
Ultra-processed, low-vegetable diets.
Quick Note:
Cruciferous vegetables are natural detox support.
6.3 Micro Minerals (Light Blue)
m1 — Iron (Fe)
Stands For: Oxygen transport mineral.
Function:
Hemoglobin, energy production, brain function.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Spinach, lentils, beans, jaggery, methi, amaranth, fortified cereals.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Vitamin C (amla, lemon, guava) with iron-rich foods.
Interferes / Blocks:
Tea/coffee with meals, excess calcium, some antacids.
Quick Note:
Always test ferritin before supplementing iron.
m2 — Zinc (Zn)
Stands For: Immunity and repair mineral.
Function:
Immunity, wound healing, skin health, hormone production.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Pumpkin seeds, peanuts, sesame seeds, chickpeas, lentils.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, chicken, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Soaking and fermenting grains and legumes reduces phytates.
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess phytates; too much supplemental zinc can block copper.
Quick Note:
Crucial for skin, hair, and immunity.
m3 — Copper (Cu)
Stands For: Iron activation mineral.
Function:
Supports iron metabolism, antioxidant enzymes, and connective tissue.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Nuts, seeds (sesame, sunflower), legumes.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, fish.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Balanced zinc intake.
Interferes / Blocks:
High-dose zinc supplements.
Quick Note:
Low copper can mimic iron deficiency.
m4 — Manganese (Mn)
Stands For: Metabolism + bone formation mineral.
Function: Supports enzyme activity, bone development, antioxidant defence, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Sources (Vegetarian): Whole grains, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, legumes.
Sources (Non-Vegetarian): Eggs, seafood.
Enhances Absorption: Balanced iron + calcium intake.
Interferes / Blocks: Excess iron, calcium, and phytates.
Quick Note: Needed in tiny amounts — easily met through whole foods.
m5 — Selenium (Se)
Stands For: Antioxidant and thyroid mineral.
Function:
Thyroid hormone activation, antioxidant defence.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Whole grains, mushrooms, sunflower seeds (content varies by soil).
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, chicken, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with vitamin E.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very high intake (supplements) – narrow safety window.
Quick Note:
Best obtained from food, not high-dose supplements.
m6 — Iodine (I)
Stands For: Thyroid hormone mineral.
Function:
Supports metabolism, energy, growth.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Iodised salt, occasional seaweed.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Adequate selenium supports thyroid hormone conversion.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very large amounts of raw goitrogenic foods (e.g., large raw cabbage/soy intake) without cooking, in people already low in iodine.
Quick Note:
Check TSH and thyroid profile before making big changes in iodine.
m7 — Chromium (Cr)
Stands For: Blood sugar regulation mineral.
Function:
Supports insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Whole grains, broccoli, spices, brewer’s yeast.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, meat, fish.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Balanced meals with protein and fibre.
Interferes / Blocks:
High-sugar diets.
Quick Note:
Can be helpful in insulin resistance, but supplements need medical guidance.
6.4 Fat-Soluble Vitamins (Yellow)
V1 — Vitamin A (Beta-carotene / Retinol)
Stands For: Vision, skin, and immunity vitamin.
Function:
Eye health, skin healing, mucosal immunity.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Carrot, pumpkin, sweet potato, spinach, other dark green and orange vegetables (with fat).
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Eat with healthy fats.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very low-fat diets, fat malabsorption issues.
Quick Note:
Plant form (beta-carotene) is safer. Retinol supplements need caution.
V2 — Vitamin D
Stands For: Bone and immunity hormone-vitamin.
Function:
Calcium absorption, immune modulation, mood support.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Sunlight exposure, UV-exposed mushrooms, some fortified foods.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, fortified dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Vitamin K2 and magnesium.
Interferes / Blocks:
Gut issues, very low-fat intake, poor sunlight exposure.
Quick Note:
Most people need to test levels and often need supplementation under guidance.
V3 — Vitamin E
Stands For: Cell protection vitamin.
Function:
Antioxidant, protects fats in cell membranes from oxidation.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Almonds, sunflower seeds, spinach, vegetable oils (unrefined).
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, fish, dairy (smaller amounts).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works well with vitamin C.
Interferes / Blocks:
Deep-fried, oxidised fats increase oxidative stress.
Quick Note:
Helps protect cell membranes and healthy fats in the body.
V4 — Vitamin K (K1 + K2)
Stands for: Clotting and bone vitamin.
Function:
Blood clotting, bone mineralization.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Green leafy vegetables, sprouts, fermented foods.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Fat + vitamin D improve use.
Interferes / Blocks:
Certain medications (e.g., blood thinners) – needs medical supervision.
Quick Note:
Works closely with calcium and vitamin D for bones.
6.5 Water-Soluble Vitamins (Pink)
W1 — Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Stands For: Energy and nerve vitamin.
Function:
Helps convert food into energy; supports the nervous system.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Whole grains, legumes, seeds.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with magnesium.
Interferes / Blocks:
Excess alcohol, heavily refined grains.
Quick Note:
Key for steady energy and nerve function.
W2 — Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Stands For: Energy metabolism and antioxidant support.
Function:
Supports energy production and helps protect cells.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Milk (for lacto-vegetarians), almonds, spinach.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, fish, dairy.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with other B vitamins.
Interferes / Blocks:
Light exposure can degrade it (store foods properly).
W3 — Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Stands For: Energy and lipid metabolism.
Function:
Supports energy production, skin health, and nervous system.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Peanuts, whole grains, legumes.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Protein-rich meals.
Interferes / Blocks:
Very high-dose supplements can have side effects.
W4 — Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Stands For: CoA production and adrenal support.
Function:
Energy metabolism and stress response support.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Mushrooms, legumes, whole grains.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, chicken, fish.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Variety of whole foods.
Interferes / Blocks:
Severe, chronic stress and very refined diets.
W5 — Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Stands For: Neurotransmitters and amino acid metabolism.
Function:
Supports nervous system and protein metabolism.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Banana, potato, chickpeas.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with magnesium.
Interferes / Blocks:
Alcohol and unmanaged stress.
W6 — Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
Stands For: Hair, nail, and metabolism support.
Function:
Supports carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Oats, nuts, seeds, sweet potato.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, dairy, liver.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Adequate protein intake.
Interferes / Blocks:
Large amounts of raw egg whites (rare in real life).
W7 — Vitamin B9 (Folate)
Stands For: DNA synthesis and pregnancy health.
Function:
Supports cell growth, red blood cell production, and fetal development.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Spinach, beetroot, chickpeas, green leafy vegetables.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs, liver.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with vitamin C and B12.
Interferes / Blocks:
Alcohol, some medications.
Quick Note:
Critical before and during pregnancy (under medical guidance).
W8 — Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Stands For: Nerve and red blood cell vitamin.
Function:
Maintains nervous system and red blood cells.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Fortified foods and supplements (true plant sources are minimal).
Animal Sources (Indian):
Dairy, eggs, liver, fish, chicken.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Healthy stomach acid and gut health.
Interferes / Blocks:
Metformin, low stomach acid, some gut disorders.
Quick Note:
Most vegetarians need B12 supplements under guidance.
W9 — Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Stands For: Immunity, collagen, and iron absorption.
Function:
Supports immunity, skin health, collagen formation, and iron absorption.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Amla, guava, citrus fruits, capsicum.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Small amounts in some organ meats.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Pair with iron-rich meals.
Interferes / Blocks:
Heat and overcooking.
Quick Note:
Best taken from fresh, minimally processed foods.
6.6 Functional Nutrients (Teal)
F1 — Omega-3 (ALA/EPA/DHA)
Stands For: Anti-inflammatory and brain-support fats.
Function:
Supports heart health, brain function, and reduces inflammation.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, algae-based supplements.
Animal Sources (Indian):
Eggs (omega-3 enriched), fish (rohu, mackerel, sardines), dairy (small amounts).
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Works with vitamin E.
Interferes / Blocks:
High omega-6 diet (excess refined seed oils).
Quick Note:
Most vegetarians benefit from an algae-based DHA supplement.
F2 — Polyphenols & Phytonutrients
Stands For: Antioxidants and cellular protection compounds.
Function:
Protects cells, reduces inflammation, supports long-term disease prevention.
Plant Sources (Indian):
Turmeric, berries, colourful vegetables, green tea, spices, herbs, dark chocolate (in moderation).
Animal Sources (Indian):
Minimal; mainly plant-derived.
Enhances Absorption / Impact:
Variety and colour on your plate.
Interferes / Blocks:
Overcooking and deep-frying.
Quick Note:
“Eat the rainbow” is really about phytonutrients, not just aesthetics.
F3 — Enzymes
Stands For: Natural catalysts that speed up digestion & metabolism.
Function: Break down carbs, protein, fats; improve nutrient absorption; reduce bloating.
Sources (Vegetarian): Papaya, pineapple, banana, ginger, fermented foods (idli/dosa batter, curd).
Sources (Non-Vegetarian): Eggs, yogurt, fish (natural digestive enzymes).
Enhances Absorption: Warm foods, probiotics.
Interferes / Blocks: Overcooked foods, very high-stress meals.
Quick Note: Fresh + fermented foods boost your natural enzyme production.
F4 — Antioxidants
Stands For: Protective molecules that reduce oxidative stress.
Function: Protect cells, lower inflammation, support skin, immunity & aging.
Sources (Vegetarian): Turmeric, berries, green tea, amla, colourful vegetables.
Sources (Non-Vegetarian): Eggs, fish, chicken (via selenium + carotenoids).
Enhances Absorption: Healthy fats + vitamin C synergy.
Interferes / Blocks: Deep-fried foods, smoking, chronic stress.
Quick Note: “Eat the rainbow” = easiest antioxidant rule.
F5 — Adaptogens
Stands For: Stress-balancing plant compounds.
Function: Support adrenal health, balance cortisol, improve resilience.
Sources (Vegetarian): Ashwagandha, tulsi, giloy, amla, ginseng, shatavari.
Sources (Non-Vegetarian): No major natural animal-based adaptogens (plants are the primary source).
Enhances Absorption: Warm water, healthy fats.
Interferes / Blocks: Excess caffeine, irregular sleep.
Quick Note: Best taken consistently — small daily doses work better than high single doses.
7. How to Use This Cheat Sheet in Daily Life
You do not need to memorise everything.
Start with three simple rules:
- Eat the colours
- Include at least 3 different colour groups (from the table) in each main meal.
- Pair nutrients smartly
- Vitamin C + Iron (amla with dal/rajma)
- Fat + Vitamins A/D/E/K (ghee or nuts with veggies)
- Probiotic + Fibre (curd + salad / veg khichdi)
- Test before supplementing
- Especially B12, vitamin D, ferritin, thyroid
- Use supplements to fill gaps, not to replace food
Over time, you will look at your plate and instantly see:
- Which nutrients are present
- Which ones are missing
- How to upgrade the same meal with simple tweaks
8. Lab Tests and Supplement Safety
Before starting any supplement, talk to your doctor about testing:
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin B12
- Ferritin and complete iron profile
- Thyroid profile (TSH, and others as needed)
Supplements are tools.
Food is the foundation.
The IntuiWell Promise
The IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™ and this cheat sheet are designed to:
- Make nutrition simple
- Keep the science clear
- Help you make intentional choices, not random ones
Each week, we will decode one nutrient tile in depth so you can transform your health — nutrient by nutrient.
Because when nutrition becomes visual and simple, staying healthy becomes easier.
10. FAQs
Q1. What is the IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™?
It is a visual, colour-coded map of key nutrients, their roles, Indian food sources, and their boosters and blockers — designed as a practical cheat sheet for everyday use.
Q2. How is this different from a normal nutrition chart?
Most charts only list nutrients and foods. This table also shows functions, absorption helpers, blockers, and real-life notes, all in one system.
Q3. Is this useful for Indian vegetarians?
Yes. The table focuses heavily on Indian plant-based sources, with animal sources listed separately. It highlights common vegetarian gaps like B12, D, and iron.
Q4. Can I plan my meals only with this table?
You can use it to spot gaps, pair foods better, and improve overall balance. For medical conditions or therapeutic diets, work with a professional.
Q5. Do I still need supplements if I follow this table?
Some nutrients, like B12 and D, are often hard to get in ideal amounts from diet alone, especially for vegetarians or people with low sun exposure. Blood tests and professional guidance decide this.
Q6. Is this table exhaustive?
No. It focuses on the most important, practical nutrients for daily health, not every trace element in biochemistry. It is a usable tool, not a textbook.
Author
Written by: Shivani Jain, Co-founder & Clinical Lead Nutritionist, IntuiWell
- Certified nutritionist based in India (Masters in Foods & Nutrition)
- Combines scientific diet planning, superfoods, ancient wisdom, and simple kitchen remedies
- Works with clients to attack the root cause of issues like fatigue, weight gain, gut problems, and hormonal imbalances
Summary
The IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™ is a visual, colour-coded nutrition system built for real Indian diets. It cuts through the noise of calorie counting and “eat healthy” clichés by mapping what each nutrient does, where to get it from Indian foods, what boosts or blocks absorption, and how nutrients work together.
The guide explains the 5 functional columns, 6 nutrient families, and gives quick mini-summaries of every macro, mineral, vitamin, and functional nutrient—without overwhelming beginners or dumbing it down for experts.
It also shows how to apply the system daily using colour diversity, nutrient pairing, and lab-test-guided supplementation. The goal: make nutrition visual, logical, and actionable—so people finally understand what their body actually needs.
FAQs
1. What is the IntuiWell Nutrient Periodic Table™?
A visual, colour-coded system that explains each essential nutrient, its function, Indian food sources, and how to improve or block absorption.
2. Why is it different from regular nutrition charts?
Because it doesn’t just list nutrients — it shows interactions, boosters, blockers, and real-life application, all in one integrated framework.
3. Is this designed for vegetarians?
Yes. It prioritizes Indian plant-based sources while clearly highlighting nutrients vegetarians commonly miss, like B12, D, and iron.
4. Can this table replace supplements?
No. It helps you optimise your diet, but some nutrients (especially B12 and D) often require testing and supplementation under professional guidance.
5. How do I actually use this in daily life?
By adding colour to your meals, pairing nutrients smartly (e.g., Vitamin C + Iron), and using the table to identify what your plate is missing.
6. Is this meant for medical diagnosis?
No. It’s an education tool. Always consult a qualified nutritionist or doctor for personalised medical decisions.
Want a personalised nutrition plan based on your deficiencies and lifestyle?
👉 Book a consultation call or request a call-back from IntuiWell today.